Multiview Geometry
Multi-view Geometry
Bundle Adjustment
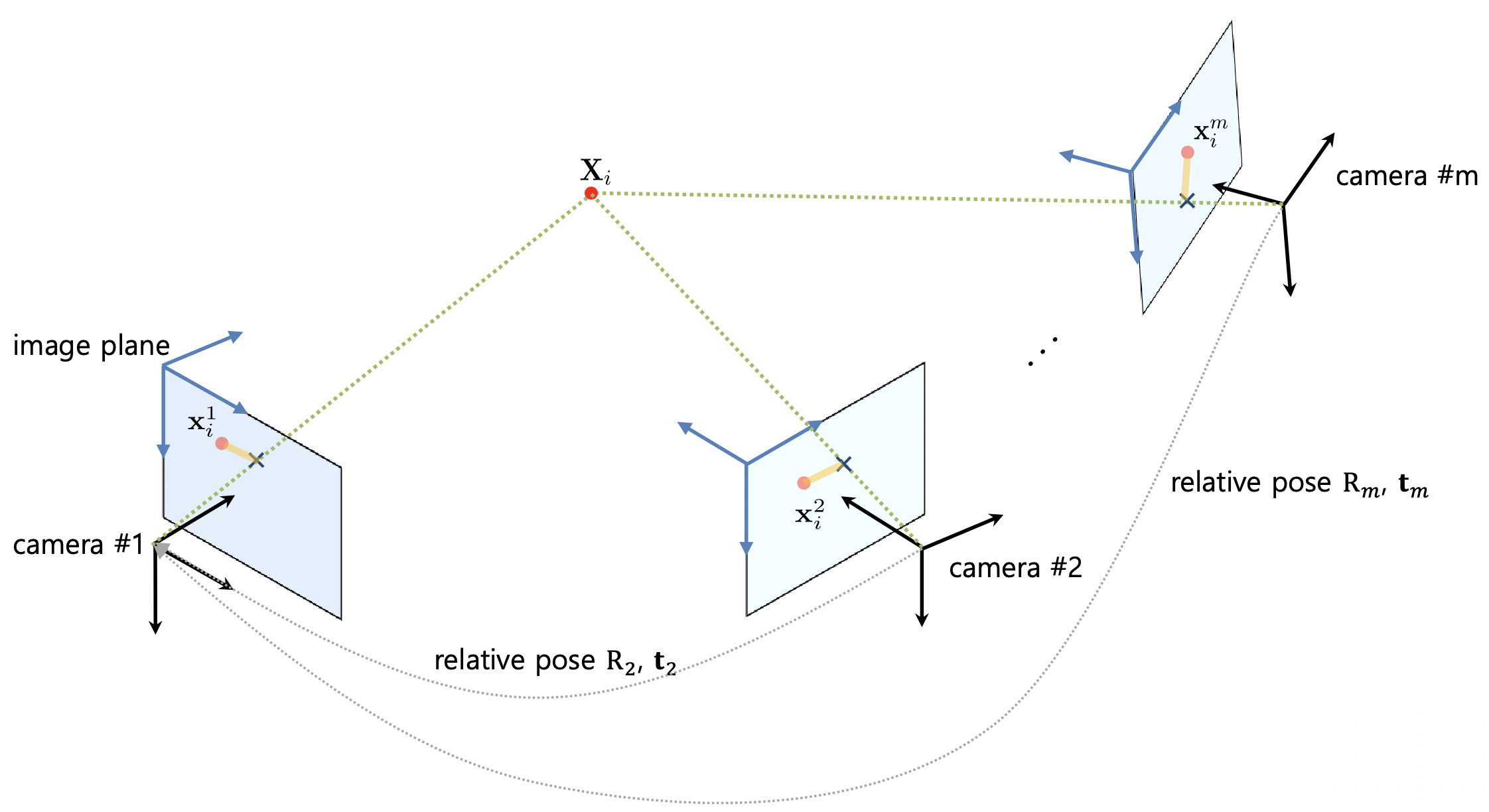
- Unknown
Position of 3D pointsandeach camera’s relative pose($6n+3m$ DoF)
- Given
- Point correspondence
- camera matrices
- position of 3D points
- each camera’s relative pose
- Constraints
- $n \times m \times \text { projection } \mathbf{x}_i^j=\mathrm{P}_j \mathbf{X}_i=\mathrm{K}_j\left[\mathrm{R}_j \mid \mathbf{t}_j\right] \mathbf{X}_i$
- Solution ⇒ Non-linear least-square optimization
- Cost Function
-
Reprojection error$\sum\limits_i^n \sum\limits_j^m v_i^j\left|\mathbf{x}i^j-\mathrm{P}_j \mathbf{X}_i\right|{\Sigma}^2 \quad \text { where } \quad v_i^j= \begin{cases}1 & \text { if } \mathbf{x}_i^j \text { is visible } \ 0 & \text { otherwise }\end{cases}$
-
- Optimization
- Levenberg–Marquardt method
- Gauss-Newton method
- Cost Function
Bundle Adjustment and Optimization Tools
- OpenCV
- No function (but cvsba is available as a sba wrapper.)
- Bundle adjustment
- (Graph) Optimization
- g2o (General Graph Optimization)
- iSAM (Incremental Smoothing and Mapping)
- GTSAM
- Ceres Solver (Google)
Applications
Structure-from-motion
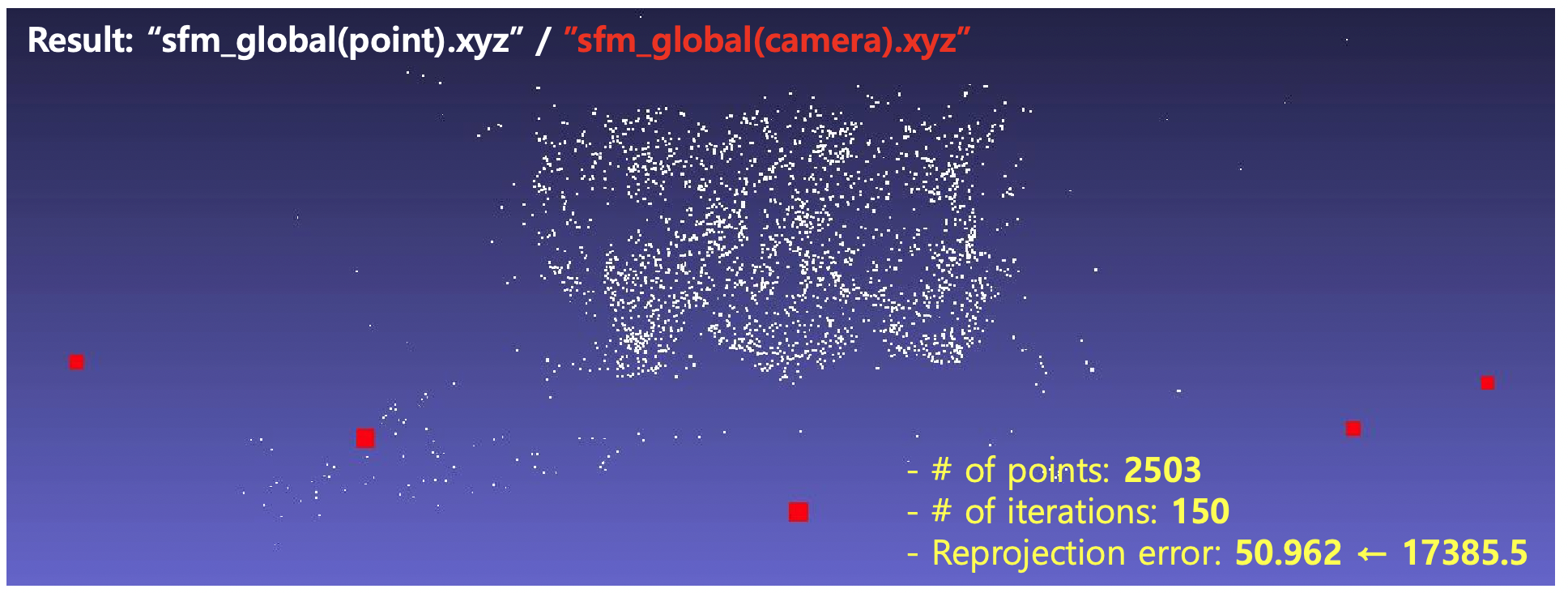
- SfM (Global)
-
Build a viewing graph (well-matched pairs) while finding inliers
⇒ Load images and extract features
⇒ Match features and find good matches (which has enough inliers)

- Initialize cameras ($R, t, f, …$)
- Initialize 3D points and build a visibility graph
-
Optimize camera pose and 3D points together (BA)

-
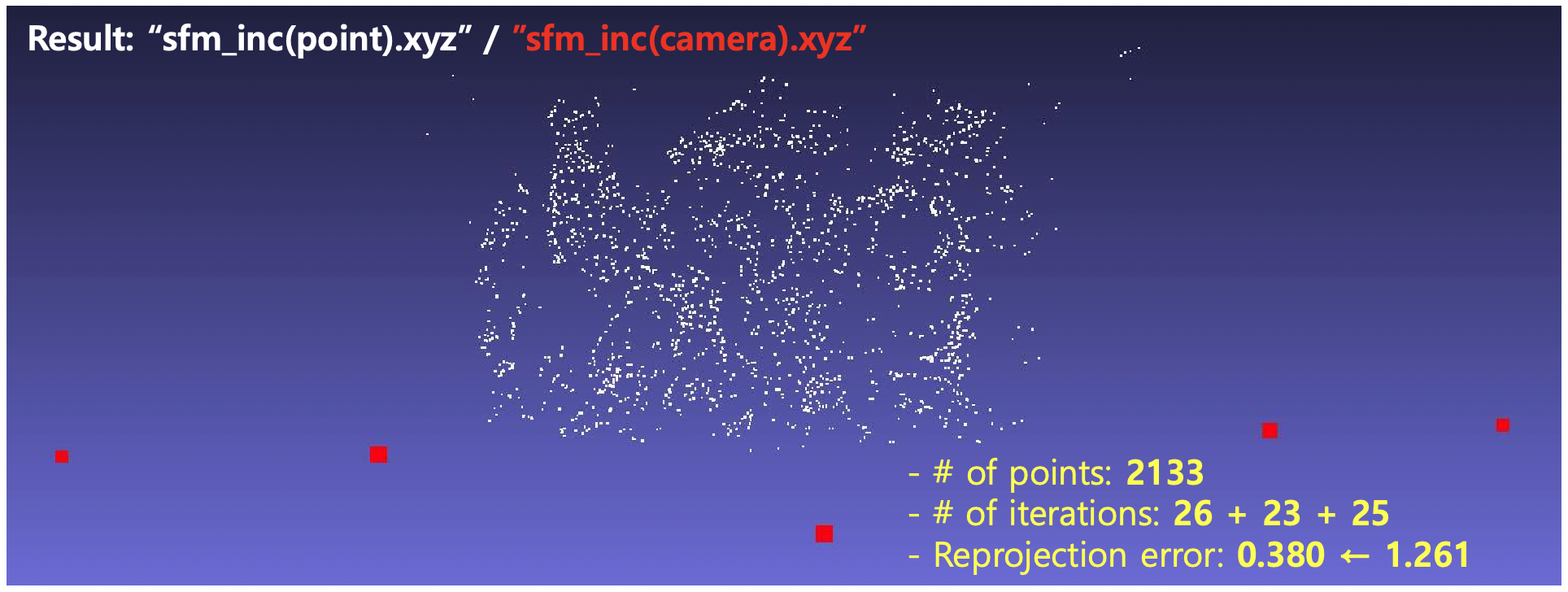
- SfM (Incremental)
- Incrementally add more views
- repeat 4~7
- Build a viewing graph (well-matched pairs) while finding inliers
- Select the best pair
- Estimate relative pose from the best two views (epipolar geometry)
- Reconstruct 3D points of the best two views (triangulation)
- Select the next image to add
⇒ Separate points into known and unknown for PnP (known) and triangulation (unknown)
- Estimate relative pose of the next view (PnP)
- Reconstruct newly observed 3D points (triangulation)
- Optimize camera pose and 3D points together (BA)

Visual SLAM
-
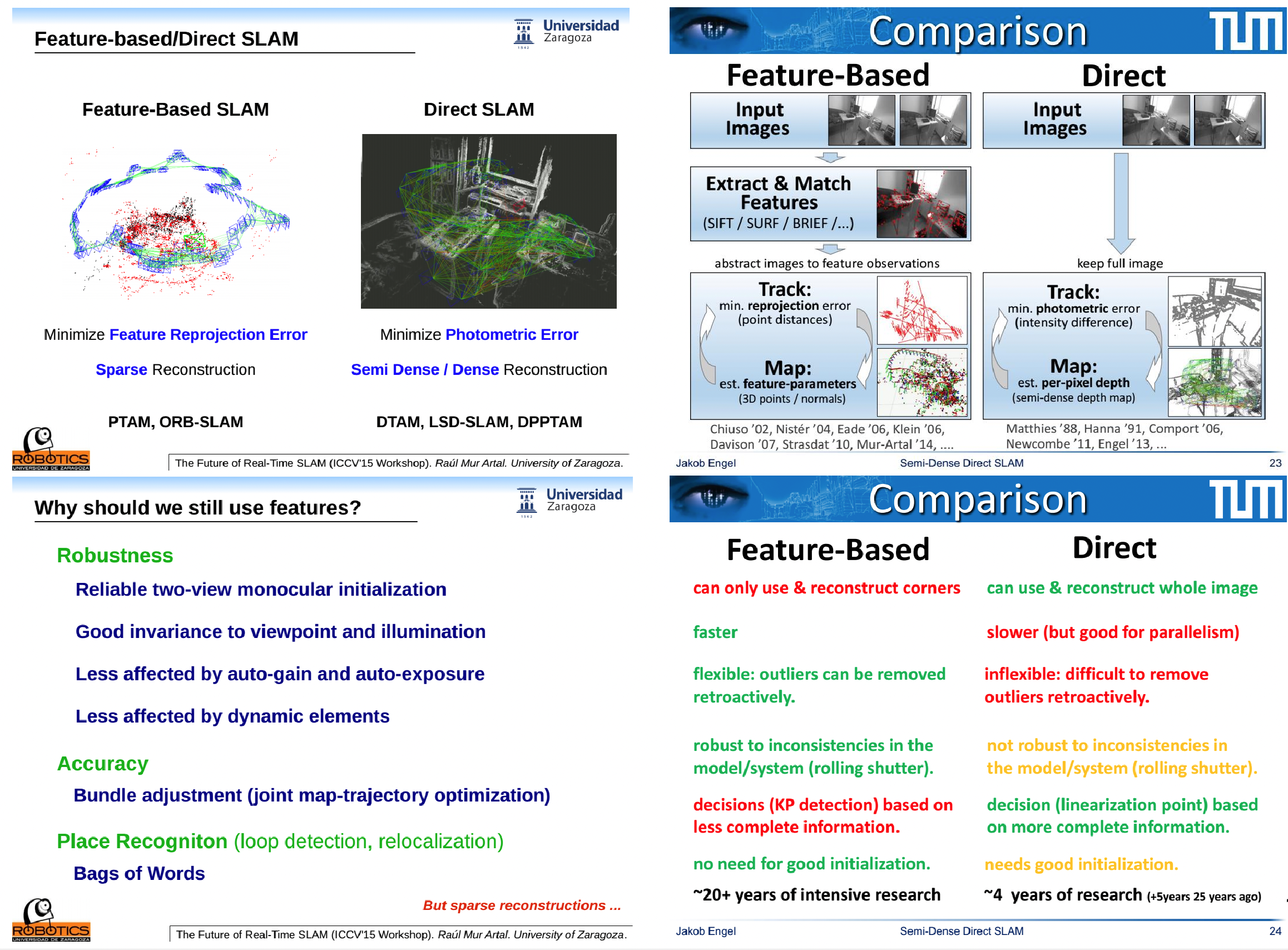
Feature-based MethodvsDirect Method
Visual Odometry
-
Visual OdometryvsWheel OdometryVisual Odometry Wheel Odometry + direct motion measure + simple calculation + six degree-of-freedoms + easy to install − heavy computation − indirect motion measure (e.g. slippage) − visual disturbance (e.g. moving objects) − two degree-of-freedoms − necessary to be on rotor/shaft Visual OdometryvsVisual SLAM- Visual Odometry
-
no assumption on trajectories
⇒ navigation / large space (outdoor)
-
- Visual SLAM
-
closed-loop is preferred for convergence
⇒ mapping / small space (indoor, campus)
-
- Visual Odometry
- Feature-based Monocular Visual Odometry
-
Two-view Motion Estimation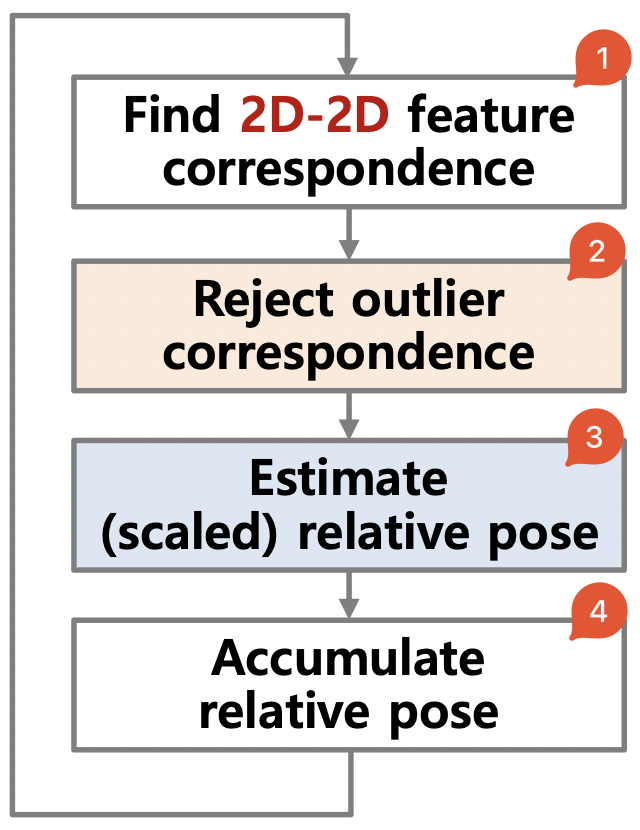
- Find 2D-2D feature correspondence
-
Feature
→ Good-Feature-to-Track [Shi94_CVPR] with bucketing to distribute features
-
Correspondence
→ Lucas-Kanade optical flow [Lucas81_IJCAI]
-
- Reject outlier correspondence
- Adaptive MSAC [Choi09_IROS]
- Iterative 5-point algorithm [Choi15_IJCAS]
-
Error measure
→ Sampson distance
- Estimate (scaled) relative pose
- Normalized 8-point algorithm
- Scale-from-ground with asymmetric kernels [Choi13_URAI]
- Find 2D-2D feature correspondence
-
PnP Pose Estimation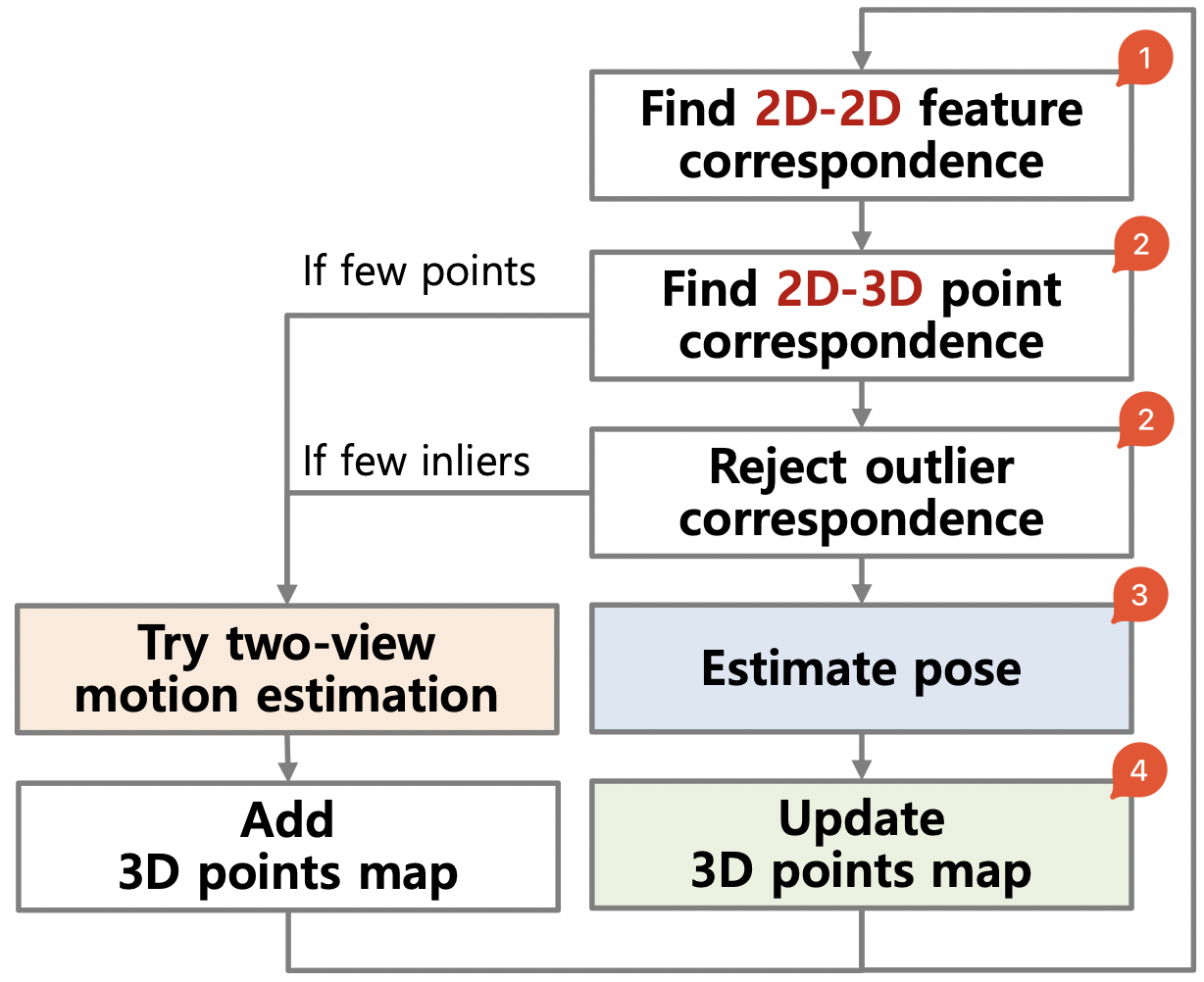
- Find 2D-2D feature correspondence
-
Feature
→ Good-Feature-to-Track [Shi94_CVPR] with bucketing to distribute features
-
Correspondence
→ Lucas-Kanade optical flow [Lucas81_IJCAI]
-
- Find 2D-3D point correspondence & Reject outlier correspondence
- Adaptive MSAC
- Iterative PnP algorithm (3-point algorithm)
-
Error measure
→ Projection error
- Estimate pose
- Iterative PnP algorithm
- Scale-from-ground with asymmetric kernels [Choi13_URAI]
- Updat 3D points map
- Bundle adjustment over last $K$ keyframes Reprojection error with Cauchy loss function
- Find 2D-2D feature correspondence
-